Pancreatitis in dogs is a condition that can cause significant discomfort and health issues, affecting the pancreas’s normal functioning.
This organ plays a critical role in digestion and regulating blood sugar, but when inflamed, it can lead to symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening illness.
Common signs of pancreatitis in dogs include;
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- abdominal pain
- lethargy
- loss of appetite
Given the pancreas’s crucial role in digesting fats, dietary management becomes a cornerstone in the treatment and management of pancreatitis.

A carefully chosen diet, typically low in fat and easily digestible, can significantly alleviate symptoms and prevent future flare-ups.
It’s vital to consult a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and a tailored dietary plan. Each dog may require a slightly different approach based on the severity of their condition, their overall health, and any concurrent medical issues.
This blog post aims to provide dog owners with comprehensive options and advice on managing canine pancreatitis through diet.
By understanding the condition and implementing a carefully considered dietary regimen, owners can play a crucial role in their pet’s health and well-being.
Understanding Pancreatitis in Dogs
What is Pancreatitis?

Pancreatitis occurs when the pancreas becomes inflamed, disrupting its ability to function properly. This inflammation can cause digestive enzymes to become active inside the pancreas, leading to self-digestion and severe pain.
In chronic cases, this condition can lead to irreversible damage and affect the pancreas’s ability to perform its essential duties, including insulin production and digestion aid.
Common Symptoms of Pancreatitis in Dogs
Dogs suffering from pancreatitis may exhibit various symptoms, such as:
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Abdominal pain, often indicated by a hunched back
- Lethargy and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Dehydration
- Fever in some cases
Symptoms can vary in intensity, from mild discomfort to severe pain and distress, necessitating immediate veterinary attention.
The Role of Diet in Managing Pancreatitis
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing and preventing pancreatitis flare-ups. Since the pancreas is involved in the digestion of fats, a low-fat diet is usually recommended to reduce the organ’s workload.
High-quality, easily digestible foods can help ensure that the pancreas is not overly stressed while still providing the dog with all the necessary nutrients.
Diet adjustments not only help manage current symptoms but also play a crucial role in preventing future episodes of pancreatitis.
Key Dietary Considerations for Dogs with Pancreatitis
Managing pancreatitis in dogs requires careful attention to their diet, as the right food choices can significantly alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
Here are some critical dietary considerations for dogs with pancreatitis:
Importance of a Low-Fat Diet
A low-fat diet is paramount for dogs with pancreatitis. Fat requires a significant amount of pancreatic enzymes to digest, and by limiting fat intake, we can reduce the strain on the pancreas.
A diet low in fat helps prevent the activation of enzymes within the pancreas that could worsen inflammation.
Veterinarians often recommend dog foods with less than 10% fat on a dry matter basis for dogs with pancreatitis, but the ideal fat content may vary based on the individual dog’s condition and tolerance.
Nutritional Components to Look for in Dog Food
When selecting dog food for a pet with pancreatitis, consider the following nutritional components:
- High-Quality Protein Sources: Protein is essential for healing and maintenance of muscle mass, especially in dogs that may have lost weight due to pancreatitis. Look for foods with easily digestible, high-quality protein sources like chicken, turkey, or fish. Avoid fatty cuts of meat and opt for lean proteins instead.
- Low-Fat Content: As mentioned, low-fat content is crucial. This doesn’t mean the food should be devoid of fat, as certain fats are essential for a dog’s health, but it should be limited to support the pancreas.
- Easily Digestible Carbohydrates: Easily digestible carbohydrates provide energy without putting too much strain on the pancreas. Ingredients like white rice and certain cooked vegetables (e.g., pumpkin, sweet potatoes) can be beneficial. However, it’s essential to introduce these gradually and in moderation to avoid upsetting the dog’s stomach.
Foods and Ingredients to Avoid
Certain foods and ingredients should be avoided in dogs with pancreatitis, including:
- High-Fat Foods: Avoid foods high in fat, such as fatty meats, butter, oils, and certain dairy products. These can exacerbate pancreatitis symptoms and lead to further inflammation.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates (e.g., corn, wheat) can be harder for dogs to digest and may strain the pancreas. Stick to simple, easily digestible carbs.
- Spicy Foods and Additives: Spicy foods and artificial additives or preservatives can irritate the digestive system and should be avoided.
- Sugary Foods: Sugary foods can lead to obesity and other health issues, which can complicate pancreatitis.
Following these dietary considerations can help manage a dog’s pancreatitis and contribute to a quicker recovery and better overall health.
It’s always important to consult with a veterinarian before making any significant changes to your dog’s diet, as they can provide personalized advice based on your dog’s specific needs and medical history.
Best Dog Food Options for Pancreatitis
When managing pancreatitis in dogs, selecting the right food is crucial for their recovery and overall well-being. Both prescription diets designed for digestive health and some over-the-counter options can be suitable.
It’s essential to work with a veterinarian to choose the best food for your dog’s specific needs.
Here’s a look at some recommended dog food brands and products, along with a discussion on the benefits of wet vs. dry food, and homemade diet options.
🍲 Ollie Dog Food for Pancreatitis Management
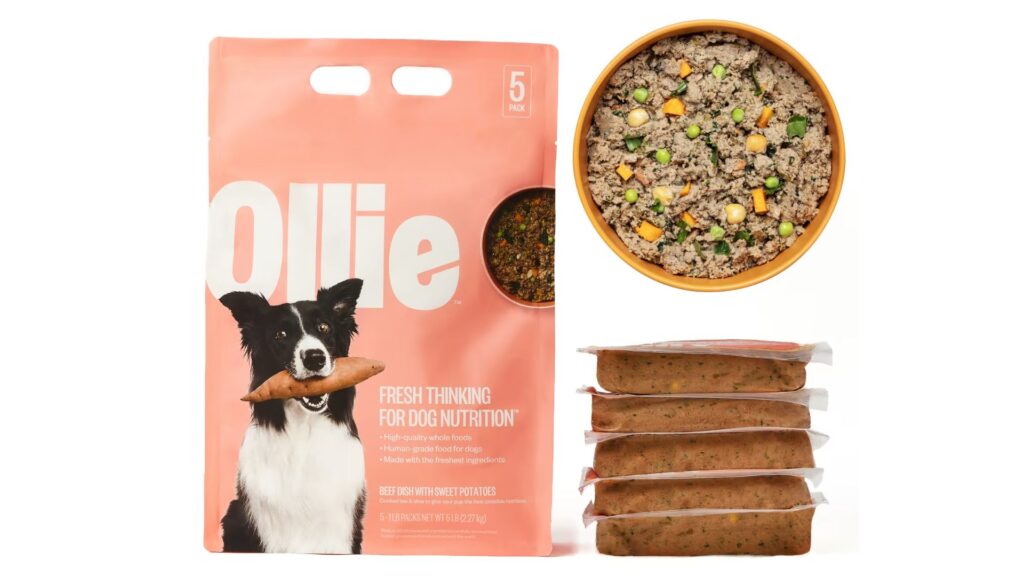

Why Choose Ollie? Ollie Dog Food stands out as a premium option for dogs with pancreatitis due to its focus on fresh, whole, and human-grade ingredients.
Each meal is specifically tailored to meet your dog’s unique nutritional needs, making it an excellent choice for pets requiring a specialized diet.
Customization and Quality:
- Personalized Plans: Ollie crafts meal plans based on your dog’s profile, including age, breed, activity level, and dietary restrictions like those needed for pancreatitis management.
- High-Quality Ingredients: Ollie’s recipes feature real, human-grade meats, vegetables, and fruits, ensuring your dog receives easily digestible and low-fat nutrition.
- Veterinarian Formulated: Meals are formulated with the guidance of veterinarians to ensure they are nutritionally balanced, supporting overall health and specific conditions like pancreatitis.
Benefits for Dogs with Pancreatitis:
- Low-Fat Recipes: Ollie offers recipes with lower fat content, crucial for dogs managing pancreatitis, to help reduce strain on the pancreas.
- Easily Digestible: The use of high-quality, fresh ingredients results in a more digestible meal, beneficial for dogs with sensitive stomachs or pancreatitis.
- Convenient Delivery: Customized meal plans are conveniently delivered to your door, making it easier to manage your dog’s pancreatitis diet.
Prescription Diets:
- Hill’s Prescription Diet i/d Digestive Care Low Fat: Specifically formulated for dogs with digestive health issues, this diet is low in fat and high in digestible proteins. It also contains prebiotic fiber to support a healthy gut microbiome.
- Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Gastrointestinal Low Fat: This formula is designed for dogs that require a very low-fat diet to manage their pancreatitis. It includes easily digestible proteins and carbohydrates to aid in digestive health.
- Purina Pro Plan Veterinary Diets EN Gastroenteric Low Fat: This diet provides balanced nutrition for dogs with pancreatitis, with a focus on low fat and high digestibility.
Over-the-Counter Options:
While prescription diets are often recommended for dogs with pancreatitis, there are over-the-counter options that might be suitable.
These include:
- Wellness CORE Natural Grain Free Reduced Fat Dry Dog Food: A grain-free, reduced-fat option that still provides high-quality protein and essential nutrients.
- Blue Buffalo Life Protection Formula Healthy Weight Adult: Formulated for weight management, this food has reduced fat content, making it a potential option for dogs with mild pancreatitis.
Wet Food vs. Dry Food for Dogs with Pancreatitis

Wet Food Benefits:
- Higher Moisture Content: Wet food can help keep dogs hydrated, which is especially important for those with pancreatitis who may be prone to dehydration.
- Often More Palatable: Dogs with a decreased appetite due to pancreatitis may be more inclined to eat wet food.
- Lower in Fat: Many wet foods are naturally lower in fat than their dry counterparts, but it’s still important to check the nutritional information.
Dry Food Benefits:
- Convenience: Dry food is easier to store and measure.
- Dental Health: Chewing dry kibble can help maintain oral health, although this is less of a concern for dogs with pancreatitis.
In many cases, a combination of wet and dry food might offer the best of both worlds, depending on the dog’s preferences and specific dietary needs.
Homemade Diet Options

Homemade diets can be tailored to meet the nutritional needs of a dog with pancreatitis, but they should be formulated with the guidance of a veterinarian or a veterinary nutritionist.
Here are some general guidelines and a simple recipe to consider:
Guidelines:
- Low Fat: Use lean meats like skinless chicken breast or turkey and low-fat dairy products.
- Easily Digestible Carbohydrates: Include cooked white rice or potatoes.
- Vegetables: Small amounts of cooked, pureed vegetables like pumpkin or carrots can add fiber and nutrients.
Simple Recipe for Dogs with Pancreatitis:
- 1 part lean protein (cooked, skinless chicken breast)
- 2 parts easily digestible carbohydrate (cooked white rice)
- A spoonful of pureed pumpkin (not pumpkin pie filling)
It’s crucial to introduce any new food gradually to avoid upsetting your dog’s stomach and to monitor their response to the diet closely.
Always consult with your veterinarian before making significant changes to your dog’s diet, especially when managing a condition like pancreatitis.
Transitioning Your Dog to a New Diet
Transitioning your dog to a new diet, especially when dealing with a sensitive condition like pancreatitis, requires a careful and gradual approach to avoid gastrointestinal upset and ensure acceptance of the new food.
Steps for a Safe Transition:
- Consult Your Veterinarian: Before making any dietary changes, discuss them with your vet, who can recommend specific foods and guide the transition process based on your dog’s health status.
- Gradual Introduction: Start by mixing a small amount of the new food with the current food. Over the course of 7-10 days, gradually increase the proportion of new food while decreasing the old food. For dogs with pancreatitis, this transition may need to be slower to allow their digestive system to adjust.
- Monitor Your Dog’s Response: Pay close attention to your dog’s appetite, stool consistency, and behavior. Any signs of discomfort, refusal to eat, vomiting, or diarrhea should be noted and reported to your veterinarian.
- Adjust as Necessary: Based on your dog’s response, the transition period can be adjusted. If your dog shows signs of discomfort, you may need to slow down the transition.
Monitoring Your Dog’s Health and Response
- Observe Clinical Signs: Watch for any changes in energy levels, appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal discomfort.
- Regular Weight Checks: Regularly weigh your dog to ensure they are maintaining a healthy weight.
- Communication with Your Veterinarian: Keep an ongoing dialogue with your vet, especially if you notice any adverse reactions or if your dog’s symptoms of pancreatitis worsen.
Additional Management Strategies
- Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Routine veterinary visits are crucial for monitoring your dog’s condition, adjusting their treatment plan as needed, and catching any potential complications early.
- Lifestyle and Exercise: Moderate, consistent exercise can help manage your dog’s weight and improve their overall health. However, dogs with pancreatitis should not be overexerted, especially during flare-ups.
- Supplements and Medications: With your vet’s guidance, certain supplements and medications may support pancreatic health and digestion. These can include digestive enzymes, probiotics, and anti-inflammatory supplements.
Conclusion/Summary
Dietary management plays a pivotal role in managing pancreatitis in dogs, significantly impacting their quality of life and ability to recover from or live with this condition.
A well-chosen diet, tailored to the individual needs of a dog with pancreatitis, can alleviate symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and support overall health.
Transitioning to a new diet should be done gradually and under the guidance of a veterinarian to ensure the best outcome for your pet.
It’s crucial for dog owners to work closely with their veterinarian to tailor a diet plan that meets their dog’s specific needs. Regular check-ups, careful monitoring, and adjustments to the diet or treatment plan are key components of managing pancreatitis effectively.
The journey of managing pancreatitis in dogs can be challenging, but with the right approach to diet and care, many dogs live happy, full lives.
Remember, the goal is not just to manage the symptoms of pancreatitis but to improve your dog’s overall health and happiness.
FAQs on Managing Canine Pancreatitis Through Diet
What signs indicate my dog’s diet is helping with their pancreatitis?
Improvements in your dog’s condition due to dietary management of pancreatitis may manifest as:
- Reduced Symptoms: Decreased vomiting, less abdominal pain, and fewer episodes of diarrhea.
- Increased Energy: A noticeable return to normal energy levels and interest in activities.
- Stable Weight: Maintenance of a healthy weight or gradual, healthy weight gain in dogs that were underweight.
- Improved Appetite: A better appetite and willingness to eat without coaxing.
- Normal Digestion: More consistent, normal stools and less gastrointestinal discomfort.
How long does it take to see improvements in my dog’s condition with a new diet?
The time frame to see improvements can vary widely among dogs with pancreatitis. Some may show signs of improvement within a few days of starting a new diet, while others may require several weeks to demonstrate noticeable changes.
Consistency with the diet and close monitoring are key during this period. If you don’t see any improvement within 7-10 days or if your dog’s condition worsens, consult your veterinarian for further advice.
Can dogs with pancreatitis ever return to a normal diet?
Whether a dog with pancreatitis can return to a “normal” diet depends on the severity of their condition, how well it’s managed, and their overall health. Some dogs may eventually tolerate a more varied diet once their pancreatitis is under control and with their veterinarian’s approval.
However, many dogs require a permanently modified diet to prevent future flare-ups. Always discuss dietary changes and long-term management strategies with your veterinarian.
Are there any breeds more susceptible to pancreatitis that should follow a specific diet?
Yes, some dog breeds have a higher predisposition to developing pancreatitis, including Miniature Schnauzers, Cocker Spaniels, and certain other small to medium-sized breeds.
These breeds may benefit from a preventive dietary approach that limits fat intake and emphasizes high-quality, easily digestible foods.
However, pancreatitis can occur in any breed, so it’s important for all dog owners to be aware of the signs and risk factors associated with the condition.
Regular veterinary check-ups can help identify any breed-specific dietary recommendations or adjustments needed to maintain optimal health.


